2-2函数的导法则
- 函数的和、差、积、商的求导法则
- 反函数的求导法则
- 复合函数的求导法则
函数的和、差、积、商的求导法则
四则运算求导法则

如果函数$u=(x)$和$v=v(x)$都在点x可导,那么它们的和、差、积、商(除分母为0的点外)都在点$x$可导,且:
- $(u \pm v)’=u’ \pm v’$
- $(uv)’=uv’+uv’$
- $(\dfrac{u}{v})’=\dfrac{u’v-uv’}{v^2}$,($v(x)\ne 0$)
推广


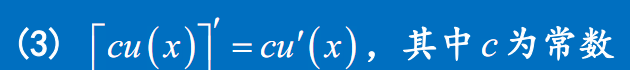
$(Cu(x))’=Cu’(x)$
例题
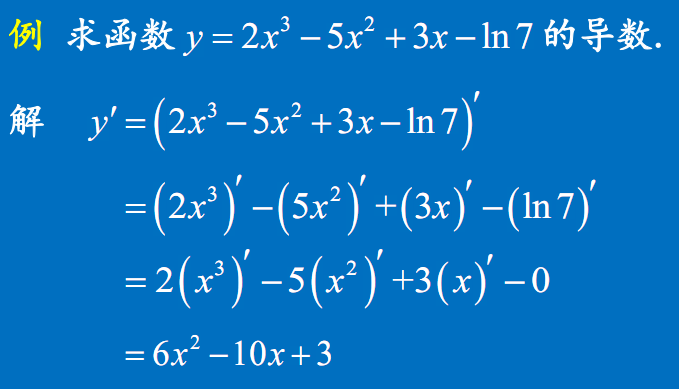
例2 自然对数的导数
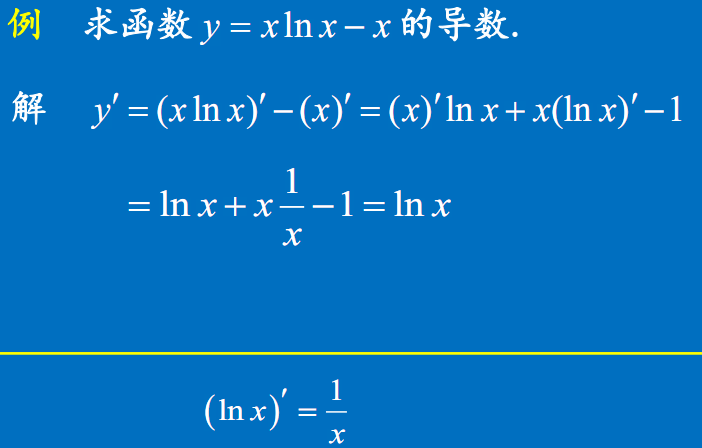
例3 正切函数的导数
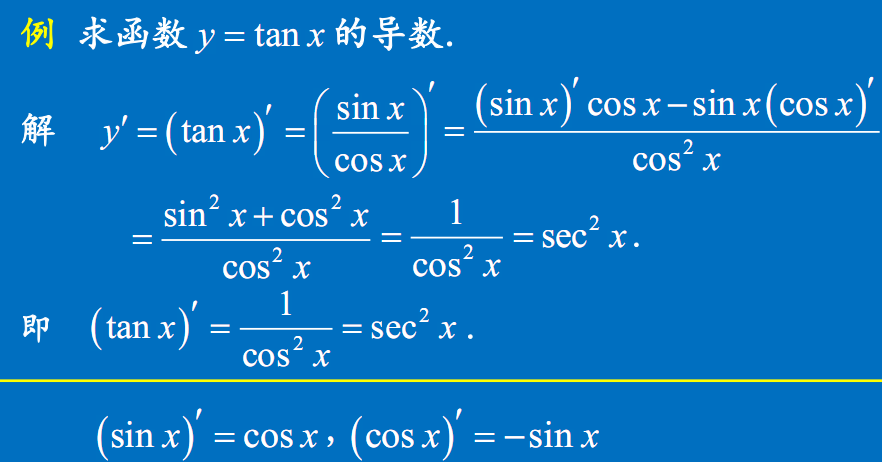
其他三角函数的导数

反函数的求导法则
定理 反函数求导法则

例题
反正弦函数的导数

其他反三角函数的导数

导数公式汇总
常数和基本初等函数的导数公式

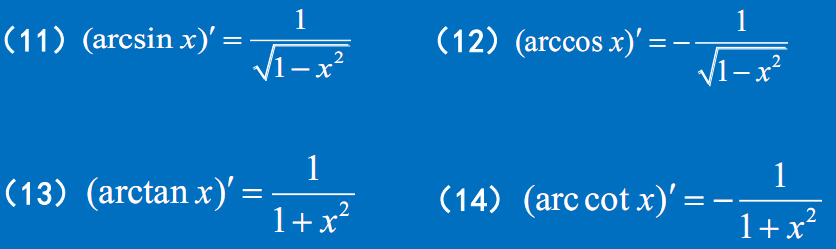
常数和基本初等函数的导数公式表
| 序号 | 导数公式 | 导数公式 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | $(C)’=0$ | $(x^u)’=ux^{u-1}$ |
| 2 | $(a^x)’=a^x\ln a$ | $(e^x)’=e^x$ |
| 3 | $(log_ax)’=\dfrac{1}{x\ln a}$ | $(\ln x)’=\dfrac{1}{x}$ |
| 4 | $(\sin x)’=\cos x$ | $(\cos x)’=-\sin x$ |
| 5 | $(\tan x)’=\dfrac{1}{\cos^2x}=sec^2x$ | $(\cot x)’=-\dfrac{1}{\sin^2x}=-csc^2x$ |
| 7 | $\int \sec x\tan xdx=\sec x+C$ | $\int \csc x cot x dx=-cscx+C$ |
| 6 | $(\sec x)’=\sec x\tan x$ | $(\csc x)’=-\csc x\cot x$ |
| 7 | $(\arcsin x)’=\dfrac{1 }{\sqrt{1-x^2}}$ | $(\arccos x)’=-\dfrac{1 }{\sqrt{1-x^2}}$ |
| 8 | $(\arctan x)’=\dfrac{1}{1+x^2}$ | $(arccot x)’=-\dfrac{1}{1+x^2}$ |
- $x’=1$
- $(x^2)’=2x$
- $(\sqrt{x})’=\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}$
- $(\dfrac{1}{x})’=-\dfrac{1}{x^2}$
复合函数的求导法则
定理 复合函数的求导法则

例题

推广

例题


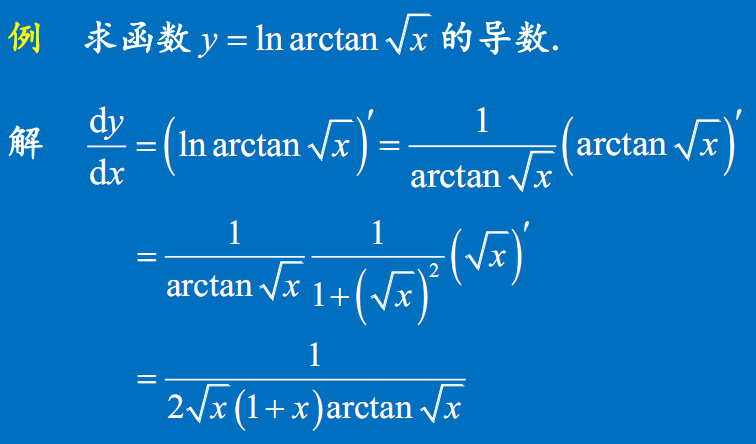
小结



习题
题1

解:
$$
\begin{aligned}
y’=&2x\ln x+(\ln x)’x^2 \nonumber \\
=&2x\ln x+ \dfrac{1}{x} x^2 \nonumber \\
=&2x\ln x+ x \nonumber \\
\end{aligned}
$$
题2

解:
$$
\begin{aligned}
y’=&(\dfrac{\ln x}{x})’ \nonumber \\
=&\dfrac{(\ln x)’x- x’\ln x}{x^2} \nonumber \\
=&\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{x} x- \ln x}{x^2} \nonumber \\
=&\dfrac{1- \ln x}{x^2} \nonumber \\
\end{aligned}
$$
题3

解:特殊三角函数值
$y’=\cos x-(-\sin x )=\cos x+\sin x$
所以:
$\left. y’\right|_{x=\frac{\pi}{6}}
=\cos \dfrac{\pi}{6}+\sin \dfrac{\pi}{6}
=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}
$
$\left. y’ \right|_{x=\frac{\pi}{4}}
=\cos \dfrac{\pi}{4}+\sin \dfrac{\pi}{4}
=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}
=\sqrt{2}
$
题4

解
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=y’
=\dfrac{1}{1+x^2}\times (1+x^2)’
=\dfrac{1}{1+x^2}\times 2x
$
题5

解:$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=f’(x^2)\times 2x$
本文链接: 2-2函数的求导法则

