概念
引例
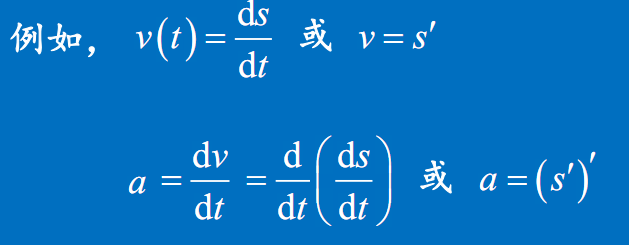
二阶导数

n阶导数

高阶导数

例1
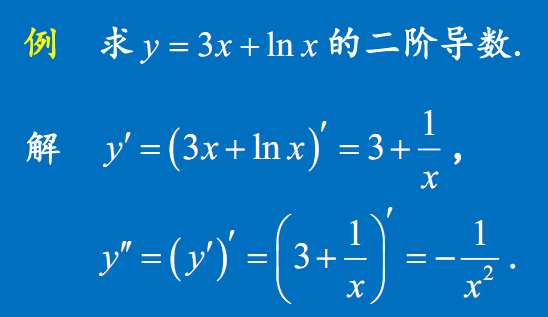
n阶导数的求法
- 直接法
- 间接法
- 公式法
1.直接法:数学归纳法
e^x的n阶导数
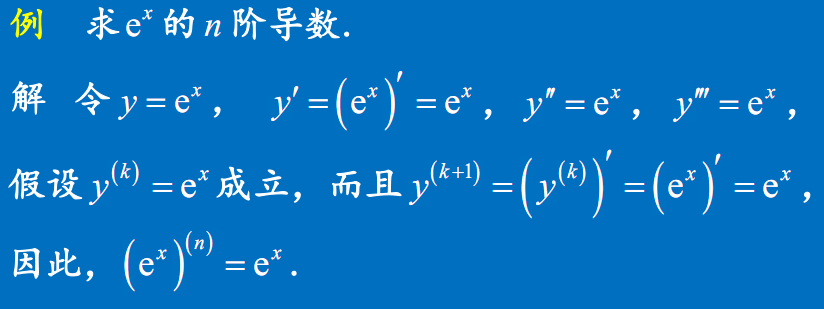
$(e^x)^{(n)}=e^x$cosx的n阶导数

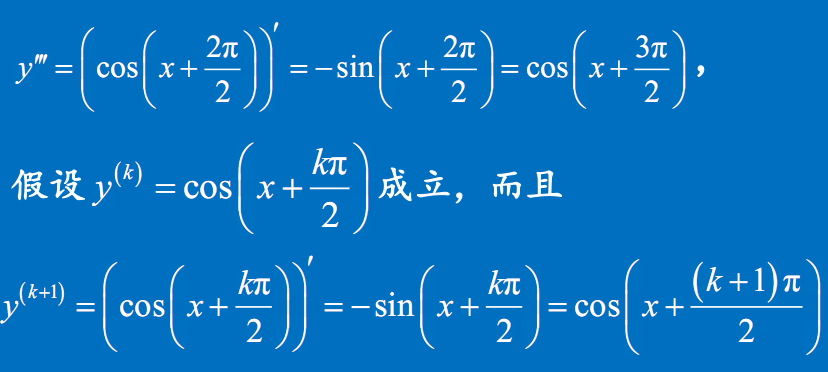
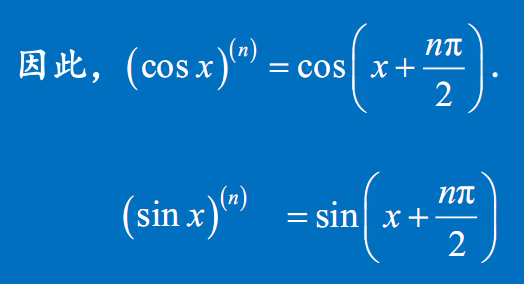
$(\cos x)^{(n)}=\cos(x+\dfrac{n\pi}{2})$
$(\sin x)^{n}=\sin(x+\dfrac{n\pi}{2})$x^u的n阶导数
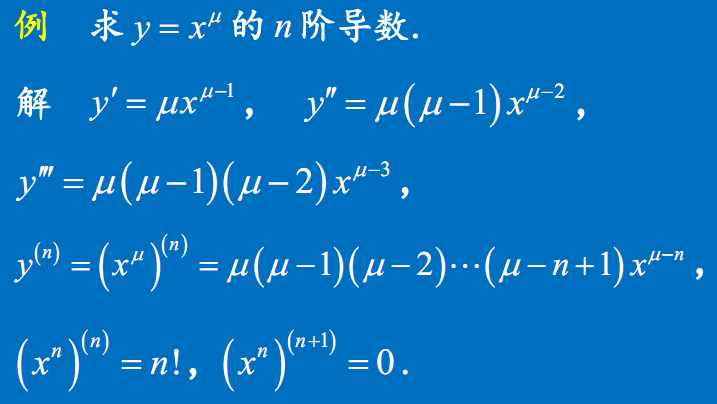
$(x^u)^{n}=u(u-1)(u-2)\cdots(u-n+1)x^{u-n}$
$(x^n)^{n}=n!$
$(x^n)^{n+1}=0$\dfrac{1}{x+a}的n阶导数
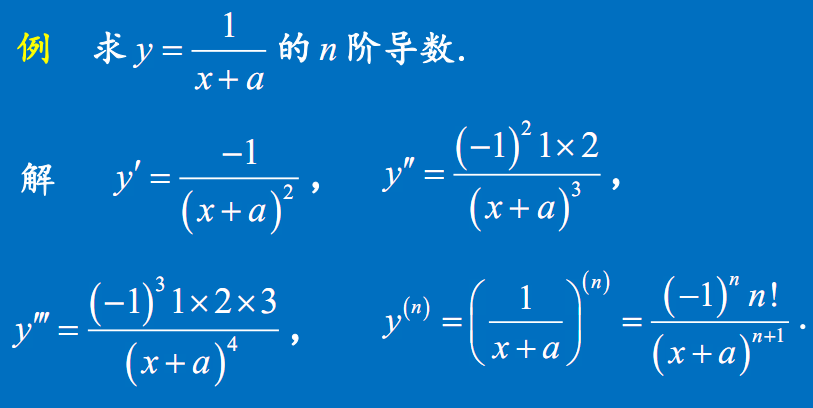
$\left(\dfrac{1}{x+a}\right)^{(n)}=\dfrac{(-1)^{(n)}n!}{(x+a)^{(n)}}$
$\left(\ln (x+b)\right)^{(n)}=\left(\dfrac{1}{x+b}\right)^{(n-1)}$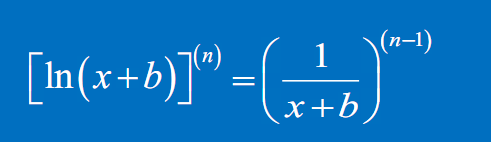
n阶可导的两个函数的和的n阶导数是各自的n阶导数之和

2.间接法

3.公式法
两个函数的乘积的n导数: 莱布尼茨公式


n阶导数公式汇总
- $\left(a^x\right)^{(n)}=a^x\ln^na$
- $(e^x)^{(n)}=e^x$
- $(\cos x)^{(n)}=\cos(x+\dfrac{n\pi}{2})$
- $(\sin x)^{n}=\sin(x+\dfrac{n\pi}{2})$
- $(x^u)^{n}=u(u-1)(u-2)\cdots(u-n+1)x^{u-n}$
- $(x^n)^{n}=n!$
- $(x^n)^{n+1}=0$
- $\left(\dfrac{1}{x+a}\right)^{(n)}=\dfrac{(-1)^{(n)}n!}{(x+a)^{(n)}}$
- $\left(\ln (x+b)\right)^{(n)}=\left(\dfrac{1}{x+b}\right)^{(n-1)}$
$$
\begin{aligned}
&\left[(a+bx)^u\right]^{(n)} \nonumber \\
=&u(u-1)(u-2)\cdots(u-n+1)b^n(a+bx)^{u-n} \nonumber \\
\end{aligned}
$$
$u=n$时:
$$
\begin{aligned}
&\left[(a+bx)^n\right]^{(n)} \nonumber \\
=&n(n-1)(n-2)\cdots(n-n+1)b^n(a+bx)^{n-n} \nonumber \\
=&n!b^n \nonumber \\
\end{aligned}
$$习题
题1

基本初等函数导数公式
解:方法1 依次求导
$y’=3\times 2x-2(-\sin x)+\dfrac{1}{x\ln a}
=6x+2\sin x+\dfrac{1}{x\ln a}
$
所以:
$y’’=6+2(\cos x)+(\dfrac{1}{x\ln a})’$
$$
\begin{aligned}
(\dfrac{1}{x\ln a})’
=& \dfrac{1’\times x\ln a- (x\ln a)’\times 1}{(x\ln a)^2 } \nonumber \\
=& \dfrac{0\times x\ln a- \ln a}{(x\ln a)^2 } \nonumber \\
=& \dfrac{- \ln a}{(x\ln a)^2 } \nonumber \\
=&-\dfrac{1}{x^2\ln a } \nonumber \\
\end{aligned}
$$
所以:
$y’’=6+2(\cos x)-\dfrac{1}{x^2\ln a }$方法2 使用公式
由n阶导数公式:
$(x^u)^{n}=u(u-1)(u-2)\cdots(u-n+1)x^{u-n}$,
$(x^n)^{n}=n!$得:
$(3x^2)’’=3\times 2!=3\times 2\times 1=6$
由$(\cos x)^{(n)}=\cos(x+\dfrac{n\pi}{2})$
三角函数$\sin x$,$\cos x$加上一个数后的符号:奇变偶不变,符号看象限.象限记不得的话可以画图像确定。
得到:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\left(-2\cos x\right)^{(2)}
=&-2\times \cos(x+\dfrac{2\pi}{2}) \nonumber \\
=&-2\times \cos(x+\pi) \nonumber \\
=&-2\times -\cos(x) \nonumber \\
=&2\cos x \nonumber \\
\end{aligned}
$$
最后一个而函数我还不知道有什么公式,所以还是按方法1计算。
题2

方法1 逐一求导
$f(x)=(ax+b)^3$
$f’(x)=3(ax+b)^2a$
$f’’(x)=3\times2(ax+b)a\times a$
$f’’’(x)=3\times2a\times a\times a=6a^3$
所以:
$f’’’(2)=6a^3$
方法2 使用n阶导数公式
$\left[(a+bx)^u\right]^{(n)}=u(u-1)(u-2)\cdots(u-n+1)b^n(a+bx)^{u-n}$
$a^0=1$
所以$\left((ax+b)^3\right)^{(3)}=3\times 2\times 1\times a^3(a+bx)^{3-3}=6a^3$
题3

遇到复杂的题及时放弃
题4

$(x^n)^{n}=n!$
所以$y^{(n)}=2n!$
题5

$$
\begin{aligned}
y’=&f’(e^{2x})(e^{2x})’ \nonumber \\
=&f’(e^{2x})2e^{2x} \nonumber \\
=&2e^{2x}f’(e^{2x}) \nonumber \\
\end{aligned}
$$
$$
\begin{aligned}
y’’=&2(e^{2x})’f’(e^{2x})+2e^{2x}f’’(e^{2x})(e^{2x})’ \nonumber \\
=&2e^{2x}2f’(e^{2x})+2e^{2x}f’’(e^{2x})(e^{2x})2 \nonumber \\
=&4e^{2x}f’(e^{2x})+4e^{2x}e^{2x}f’’(e^{2x}) \nonumber \\
=&4e^{2x}f’(e^{2x})+4e^{2x+2x}f’’(e^{2x}) \nonumber \\
=&4e^{2x}f’(e^{2x})+4e^{4x}f’’(e^{2x}) \nonumber \\
\end{aligned}
$$
本文链接: 2-3高阶导数

